Each spinal segment is like a well-tuned part of a machine. All of the parts should work together to allow weight bearing, movement, and support. A spinal segment is composed of two vertebrae attached together by ligaments, with a soft disc separating them. The facet joints fit between the two vertebrae, allowing for movement, and the foramen between the vertebrae allows space for the nerve roots to travel freely from your spinal cord to the rest of your body. When all the parts are functioning properly, the spinal segments join to make up a remarkably strong structure called the spine. When one segment deteriorates to the point of instability, it can lead to localized pain and difficulties.
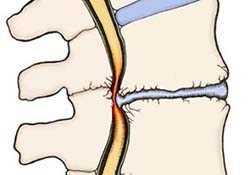
Segmental instability occurs when there is too much movement between two vertebrae in your spine. The excess movement of the vertebrae can cause pinching or irritation of nerve roots. It can also cause too much pressure on your facet joints, leading to inflammation of facet joints. It also may cause muscle spasms as the paraspinal muscles in your back try to stop the spinal segment from moving too much. The instability eventually results in faster degeneration of your spine in this area.
Causes
Your spine is stabilized by an intricate set of systems working in concert to both limit and allow flexibility in your spine. These systems are:
The passive system – which includes your vertebrae, facet joints, intervertebral discs, and ligaments. This system stabilizes your spine when you bend and twist.
The active system – which includes the muscles and tendons that are attached to your spine. This system stabilizes your spine when it is in the neutral zone (neither bent nor twisted).
The neural system – which includes the nerves that control the muscles in your spine. This system receives input from the other systems to determine what your spine requires to maintain stability when it is in motion and when it is neutral.
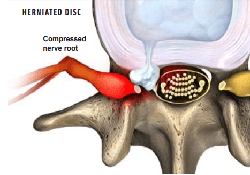
These 3 systems of spinal stability must work together at all times to keep your spine strong and safe. If a problem occurs in any one of the systems, such as a fractured vertebra, a herniated disc, a muscle strain or tendon sprain, or a pinched nerve (called radiculopathy), this puts added stress on the remaining systems to keep your spine stable.
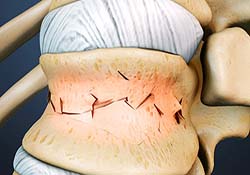
It is hard to determine which problem comes first in segmental instability. In some cases, degeneration of a disc in your spine begins the process. Once the disc is no longer able to function normally, the degeneration process of ALL parts of the spinal segment begins. As your disc continues to degenerate, the facet joints become arthritic, bone spurs form around the joints, and the segmental instability gets worse. This cycle continues until it is corrected.
Segmental instability of your spine can also result post-operatively after spinal surgery and after trauma to your spine. It can also be caused by other conditions including scoliosis, infection, and tumors.
Symptoms
Low back pain is a common symptom reported by up to 30% of patients with segmental instability. The pain you feel when you have segmental instability may be chronic, which means you feel it all the time, or it may recur either with certain movements or when you hold your back still. The pain may come on suddenly and in response to a movement that normally would not be painful. You may also feel like popping or cracking your back would make the pain feel better. If you have segmental instability, you may also feel like your back is weak, or that it catches or locks when you move.
Diagnosis
The first step in diagnosing segmental instability is to perform a complete history and physical exam. Your doctor may ask you about your history of low back pain and back trauma and how it has been treated in the past. During the physical exam your doctor will check how your back works through various types of motion. To diagnose your back problem, your doctor may also ask you to wear a back brace for awhile to see whether it provides relief of your symptoms. If the brace provides pain relief, this suggests you may have segmental instability.
Diagnosing segmental instability can be difficult because there is not a agreed standard on what other types of diagnostic tests to perform. This is because radiologic tests cannot show how your spine works throughout the entire range of motion.
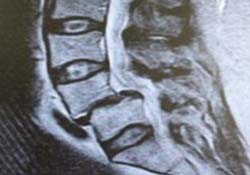
Your doctor will likely take X-rays of your spine in the neutral position (standing straight) and at different degrees of flexion. X-rays will show your doctor the amount of space between your facet joints and the condition of your vertebrae. Other diagnostic tests your doctor may perform include a CT scan to get a better look at your vertebrae and facet joints including any bone spurs that may be present. An MRI may also be ordered to check for lesions such as a herniated disc. Your doctor may also order an electromyogram (EMG) of your spine to check for signs of segmental instability.
Treatment Options
Conservative Treatment
If you have been diagnosed with segmental instability, your doctor will likely recommend conservative treatment to start. Conservative treatments for segmental instability include the use of a brace to support and stabilize your spine. Your doctor will also likely recommend physical therapy including stabilization exercises to strengthen and control the muscles in your spine, and education about how to protect your spine during everyday activities.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to correct segmental instability is usually reserved for patients with severe spinal disability after conservative treatment has failed to provide adequate relief. Spinal fusion may be recommended if one of the vertebra in your spine is able to move out of alignment by more than 4 mm (millimeters) or if the vertebra is able to rotate 10 degrees or more compared to the other vertebrae in your spine. Spinal fusion will correct the instability in your spine by permanently connecting the unstable segment to the stable segment above or below it.